Off Grid Low frequency inverter charger
May 24,2025
Understanding Low Frequency Inverters
A low-frequency inverter dose not mean 50hz or 60hz frequency ,but means transformer-based device designed to convert DC power into AC at lower voltage and frequency levels. Unlike high-frequency inverters, these models excel at managing heavy power surges and sustaining high-load operations over extended periods. The built-in transformer enhances stability, making them ideal for demanding applications.
Additionally, low-frequency inverters typically operate at 50Hz or 60Hz, aligning with regional electrical standards. For instance:
60Hz is common in the Americas.
50Hz is standard in Asia, Europe, and Africa.
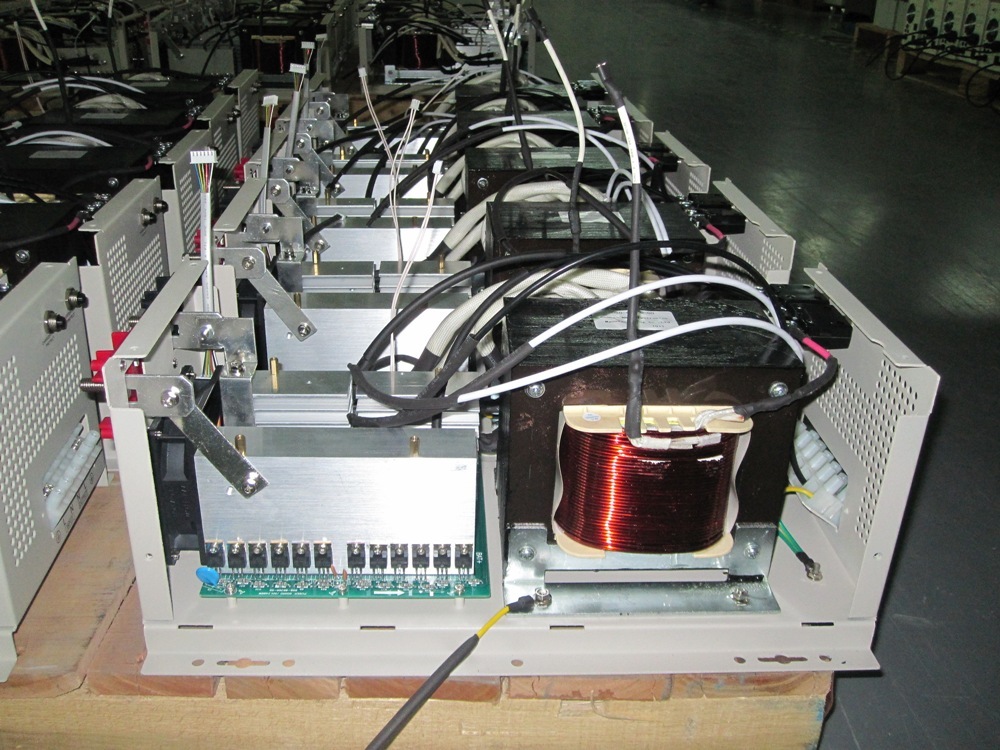

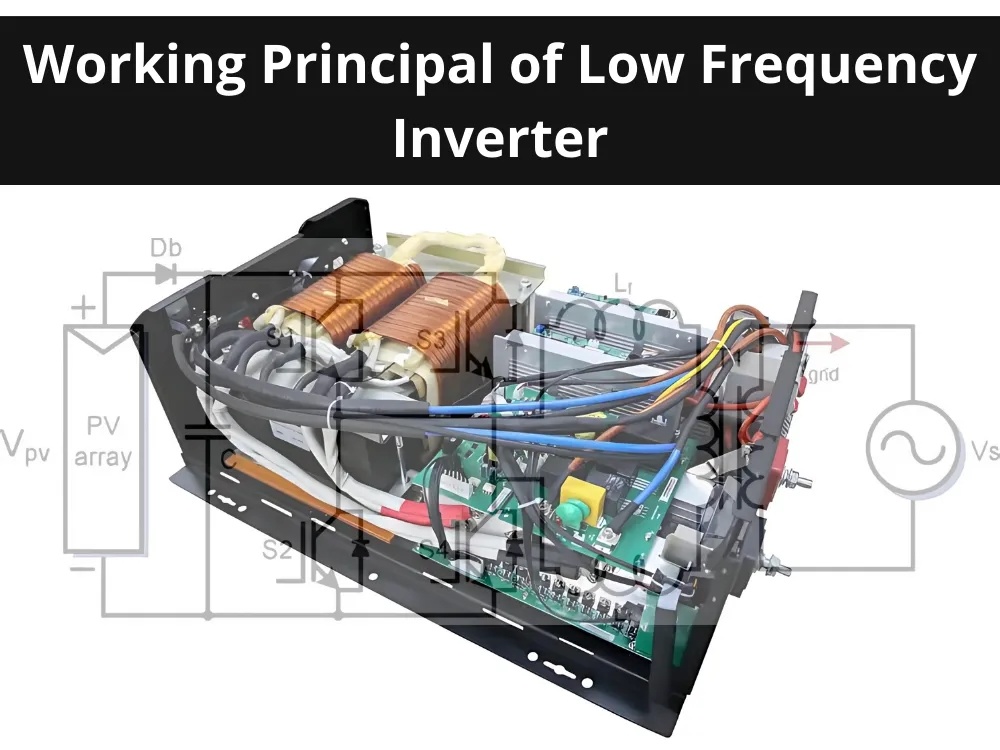
How Low Frequency Inverters Work
The conversion process involves several key stages:
DC Input: The inverter receives DC power from a source (e.g., solar panels or batteries).
Voltage Boost: The DC voltage is elevated to a higher level.
AC Conversion: Electronic switches (MOSFETs or IGBTs) transform the DC into a preliminary AC waveform.
Transformer Adjustment: The AC passes through a low-frequency transformer, which fine-tunes the voltage and provides electrical isolation to safeguard against surges.
Output Delivery: The refined AC power (pure or modified sine wave) is distributed to connected devices.
Pros and Cons of Low Frequency Inverters
Advantages
Robust Performance: Handles high power loads and surges efficiently.
Enhanced Durability: Transformers improve heat resistance, extending lifespan.
Stability: Ideal for continuous high-power applications and harsh environments.
Electrical Isolation: Protects devices from voltage spikes and interference.
Smart Controls: Microprocessors adjust output based on demand and conditions.
Disadvantages
Higher Cost: Large transformers increase production expenses.
Bulkier Design: Less portable due to size and weight.
Limited Efficiency at Low Loads: Optimized for heavy-duty use, not small-scale applications.
Noise: Transformers may hum under excessive load or imbalance.
Maintenance: Repairing transformers can be costly (well, transformer hardly go problem).
Applications of Low Frequency Inverters
Thanks to their resilience, these inverters are suited for:
Solar Power Systems: Ensures stable energy management for high-demand setups.
Industrial Equipment: Powers motors, compressors, and pumps reliably.
Vehicles: Used in RVs, boats, and electric trucks.
Off-Grid Locations: Supports remote cabins, clinics, and rural electrification.
Residential Use: Ideal for homes requiring steady, high-capacity power.



Related products
More News
Subscribe
Check the latest news of our company anytime and anywhere.
Contact ZLPOWER

1-2 Floor, Building E, Liyukeng Industrial Zone, Beihuan Road, Shangwu Community,Shiyan Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen,Guangdong, China









